Welcome to A4liveCell Blog #9! The Free Radical Theory of Ageing Ageing is an intrinsic biological process characterized by the gradual decline in cellular and molecular function over time. It involves disruptions in normal cellular mechanisms, the buildup of damaged molecules and toxins, changes in gene expression, and weakened immune and stress responses. Although extensively […]
Category: Scientific support
A4liveCell Blog#8 “Deciphering the inside cell´s story by CYTOCHECK SPAchip®!
Welcome to A4liveCell Blog #8! Cell Senescence & the Links to Homeostasis of Calcium, pH, and Oxidative Stress As our understanding of cellular biology evolves, one of the most compelling areas of research is the phenomenon of cellular senescence—a state of permanent cell cycle arrest that occurs when cells experience stress or damage. Factors such […]
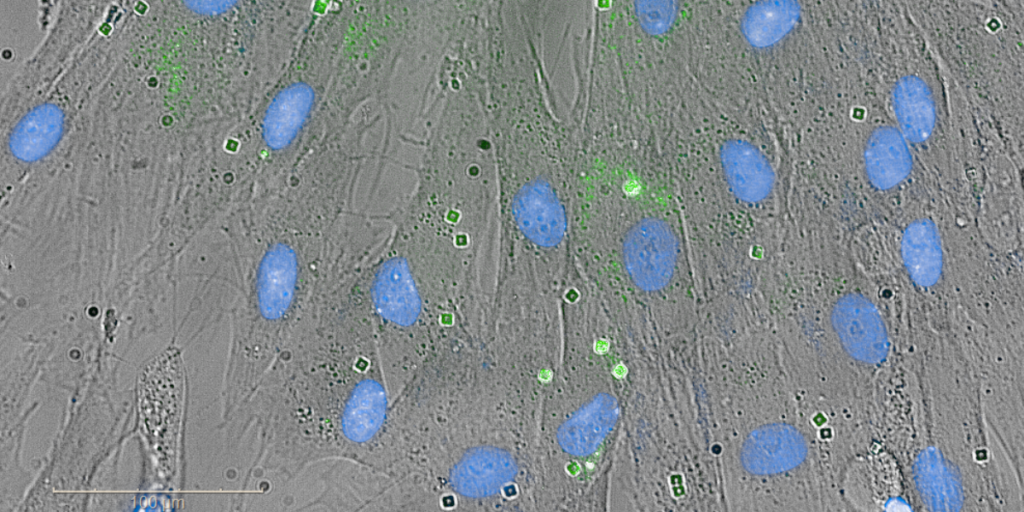
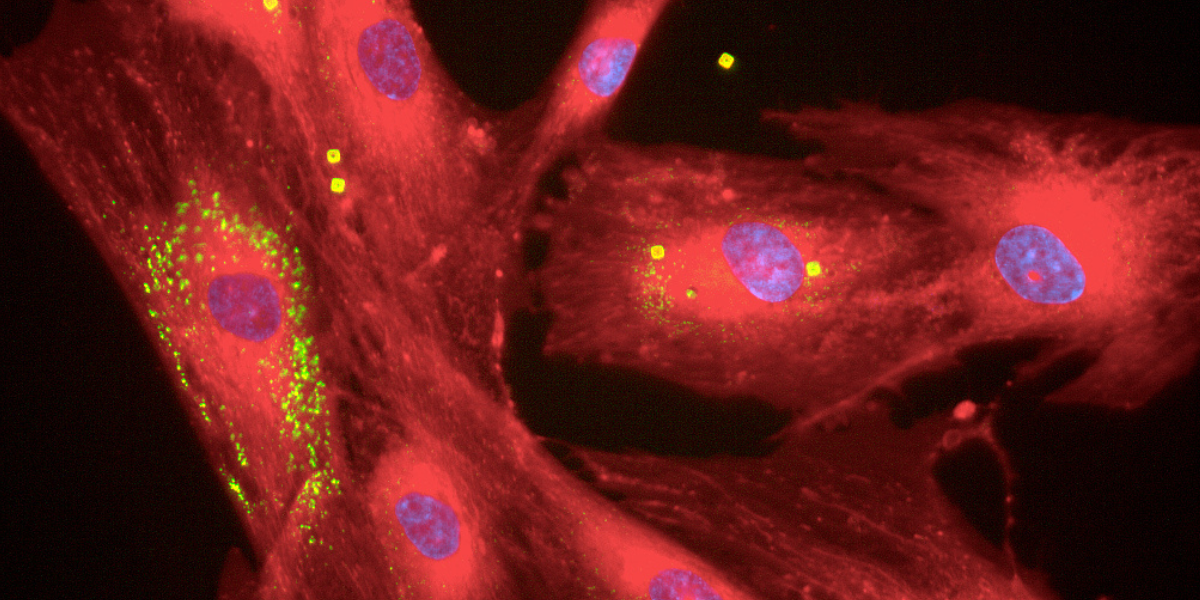
Investigating Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in fibroblast cells using SPAchip®
IntroductionReactive oxygen species (ROS) are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen that play a dual role in cellular biology. At controlled levels, ROS participate in signaling pathways crucial for normal physiological functions such as cell growth and defense mechanisms. However, excessive ROS production leads to oxidative stress, which has been linked to cellular damage, inflammation, aging, […]
A4liveCell Blog#7: “Deciphering the inside cell´s story by CYTOCHECK SPAchip®!
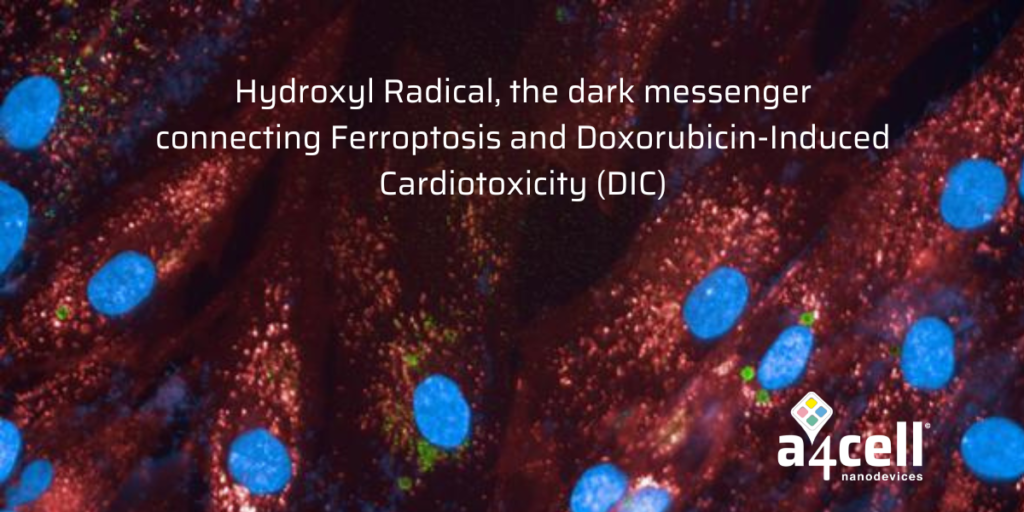
Welcome to A4liveCell Blog #7! Hydroxyl Radical, the dark messengerconnecting Ferroptosis and Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity (DIC) The connection between ferroptosis and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity (DIC) has emerged as a critical area of research, offering new insights into the underlying mechanisms of this cardiac toxin and how to address its adverse effects in cancer patients. Doxorubicin (DOX) is […]
A4liveCell Blog#6: “Deciphering the inside cell´s story by CYTOCHECK SPAchip®!
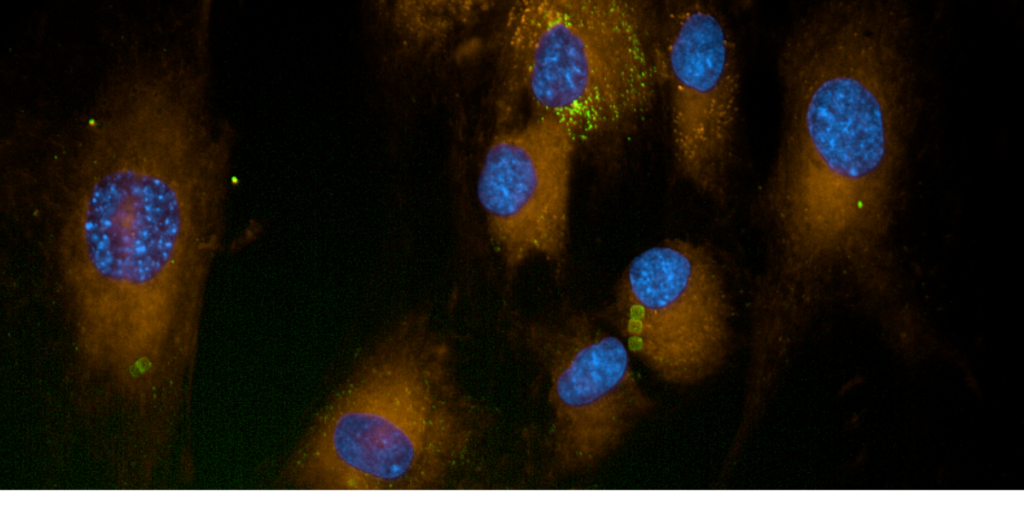
Welcome to A4liveCell Blog #6! SPAchip® as an image-based real-time readout of metabolic activity in genetic screening Understanding how the genetic information give rise to the phenotype, and how genomic perturbation affects a given phenotype are some of the main objectives of genetic screening. Recently, microscopy or FACS-based screening have emerged as new option to […]
SPAchip®: intracellular living sensors.
The power of multiplexed live analytics in cell biology Cells are continuously challenged by insults and stimuli, including drugs and xenobiotics, from the extracellular environment. In response to these challenges, a series of intracellular molecules and ions act as signalling mediators, effectors or transducers which will ultimately result into physiological changes. In this context, noteworthy […]